Run using a genomic surveillance configuration
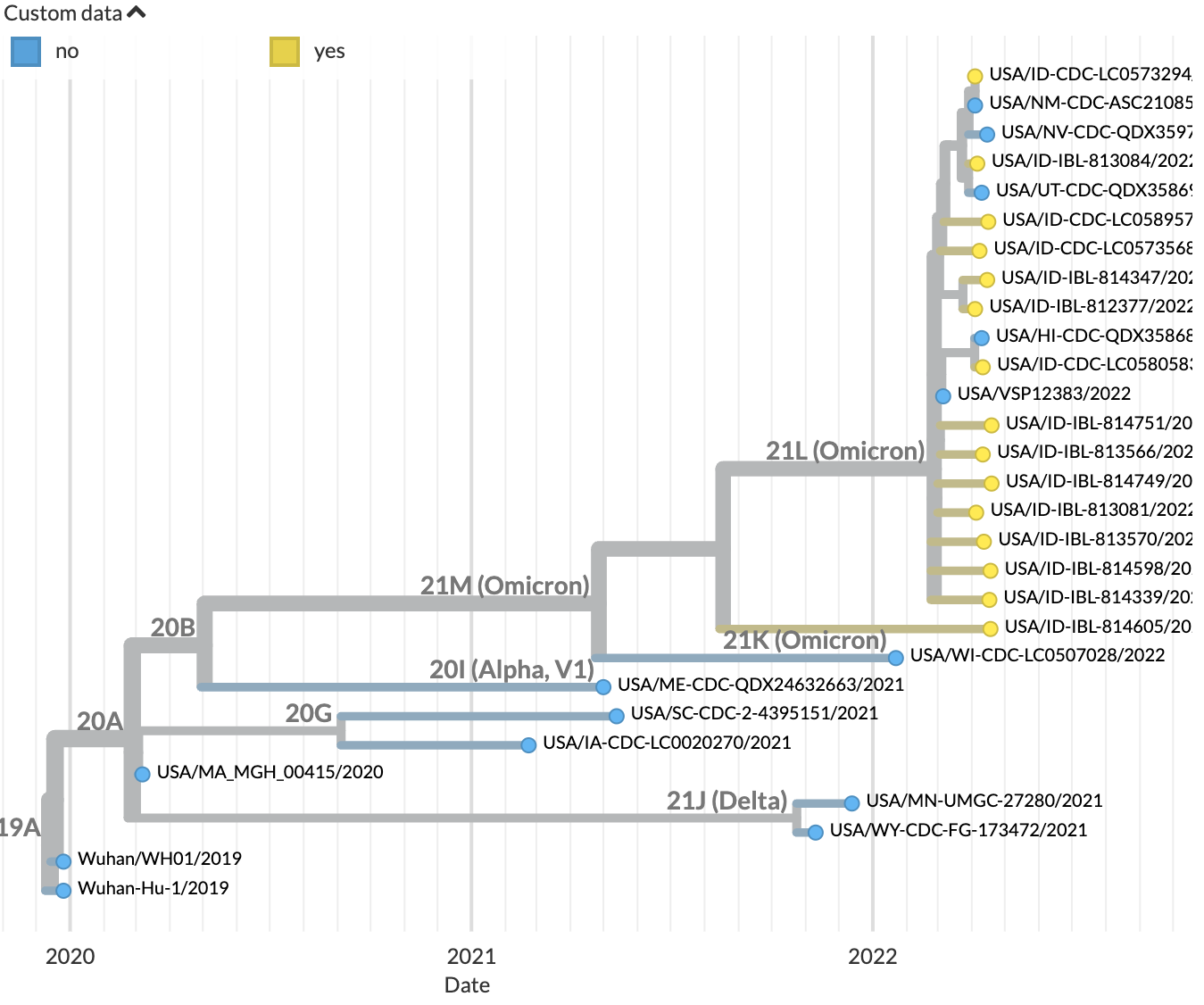
In the previous tutorial, you learned how to analyze a small set of GISAID (“custom”) data in the context of a small set of reference data. For genomic surveillance applications, you will often focus your analysis on a set of data specific to your question of interest. For example, an analysis of SARS-CoV-2 circulation in a specific geographic area requires a focal set of sequences and metadata from that area.
In this tutorial, you will learn to define and analyze a focal set of data from a geographic division in the United States using a global genetic context. You will also learn how to define a genetic context that prioritizes sequences that are genetically similar to your focal set.
Table of Contents
Prerequisites
Run using custom data. This tutorial introduces concepts expanded by the following tutorial.
Register for a GISAID account, if you do not have one yet. However, registration may take a few days. Follow alternative data preparation methods in place of Curate data from GISAID, if you wish to continue the following tutorial in the meantime.
Setup
If you are not already there, change directory to the ncov directory:
cd ncov
Curate data from GISAID
We will download a focal set of Idaho sequences from GISAID’s EpiCoV database.
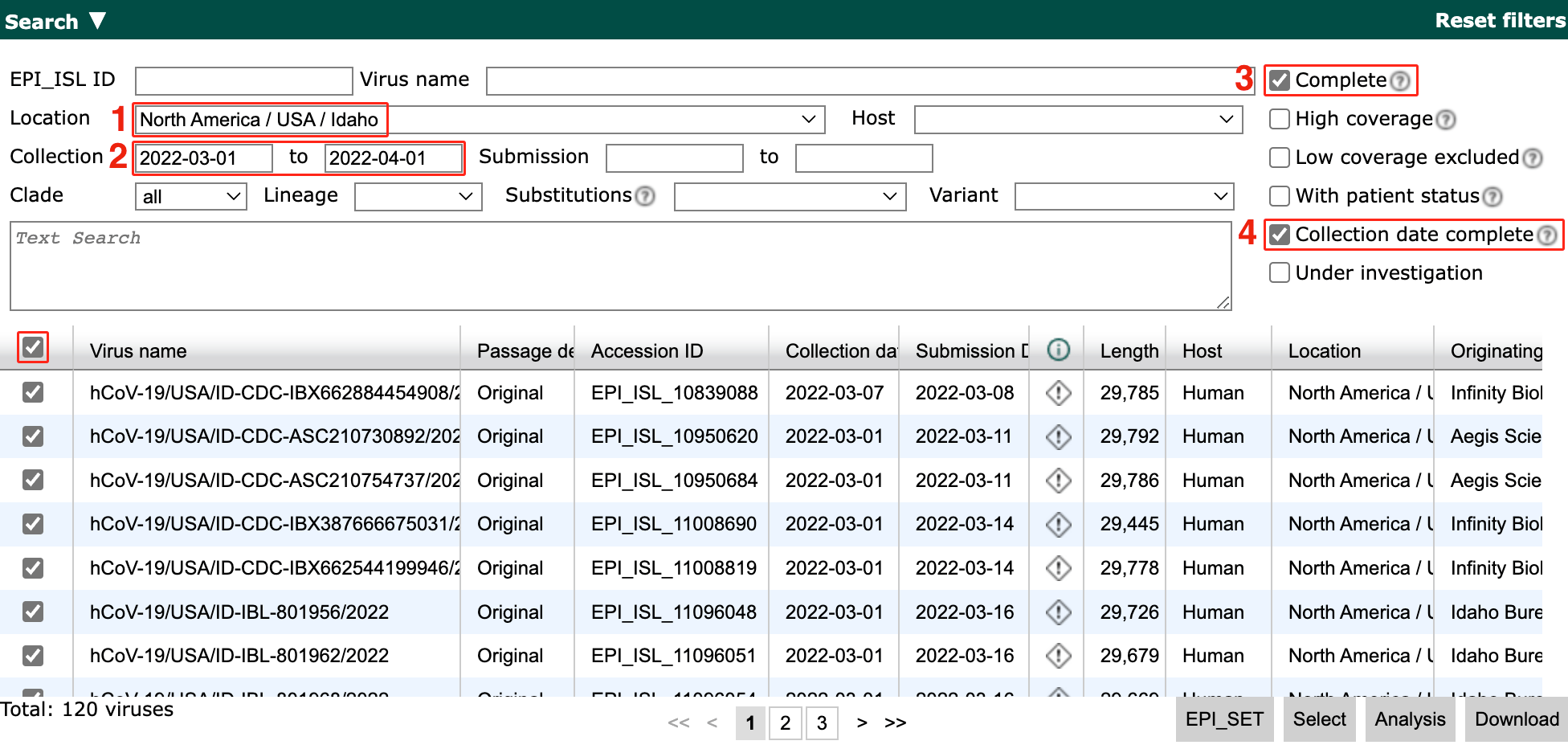
Navigate to GISAID, Login, and go to EpiCoV > Search.

Filter to sequences that pass the following criteria:
From North America / USA / Idaho
Collected between 2022-03-01 and 2022-04-01
Has a complete genome
Has an exact collection date
Note
If your selection has more than 250 sequences, adjust the minimum date until it has 250 sequences or less. This ensures the tutorial does not take too long to run.
Select the topmost checkbox in the first column to select all sequences that match the filters.
Select Download > Input for the Augur pipeline > Download.
Download/move the
.tarfile into thencov/data/directory.Extract by opening the downloaded
.tarfile in your file explorer. It contains a folder prefixed withgisaid_auspice_input_hcov-19_containing two files: one ending with.metadata.tsvand another with.sequences.fasta.Rename the files as
idaho.metadata.tsvandidaho.sequences.fasta.Move the files up to the
ncov/data/directory.Delete the empty
gisaid_auspice_input_hcov-19_-prefixed folder and the.tarfile if it is still there.
Run the workflow
From within the ncov/ directory, run the ncov workflow using a pre-written config file:
nextstrain build . --configfile ncov-tutorial/genomic-surveillance.yaml
Break down the command
The workflow can take several minutes to run. While it is running, you can investigate the contents of genomic-surveillance.yaml (comments excluded):
inputs:
- name: reference_data
metadata: https://data.nextstrain.org/files/ncov/open/reference/metadata.tsv.xz
aligned: https://data.nextstrain.org/files/ncov/open/reference/aligned.fasta.xz
- name: custom_data
metadata: data/idaho.metadata.tsv
sequences: data/idaho.sequences.fasta
- name: background_data
metadata: https://data.nextstrain.org/files/ncov/open/north-america/metadata.tsv.xz
aligned: https://data.nextstrain.org/files/ncov/open/north-america/aligned.fasta.xz
refine:
root: "Wuhan-Hu-1/2019"
builds:
idaho:
title: "Idaho-specific genomic surveillance build"
subsampling_scheme: idaho_scheme
auspice_config: ncov-tutorial/auspice-config-custom-data.json
subsampling:
idaho_scheme:
custom_sample:
query: --query "(custom_data == 'yes')"
max_sequences: 50
usa_context:
query: --query "(custom_data != 'yes') & (country == 'USA')"
max_sequences: 10
group_by: division year month
priorities:
type: proximity
focus: custom_sample
global_context:
query: --query "(custom_data != 'yes')"
max_sequences: 10
priorities:
type: proximity
focus: custom_sample
This configuration file is similar to the previous file. Differences are outlined below, broken down per configuration section.
inputs
The file paths in the second input are changed to
idaho.metadata.tsvandidaho.sequences.fasta.There is an additional input
background_datafor a regional North America dataset built by the Nextstrain team, for additional context.
builds
The output dataset is renamed idaho, representative of the new custom data in the second input.
The title is updated.
There is a new entry
subsampling_scheme: idaho_scheme. This is described in the following section.
subsampling
This is a new section that provides a subsampling scheme idaho_scheme consisting of three subsamples. Without this, the output dataset would use all the provided data, which in this case is thousands of sequences that are often disproportionally representative of the underlying population.
custom_sampleThis selects at most 50 sequences from the
custom_datainput.
usa_contextThis selects at most 10 sequences from the USA from the
background_dataandreference_datainputs.Sequences are subsampled evenly across all combinations of
division,year,month, with sequences genetically similar tocustom_sampleprioritized over other sequences.
global_contextThis selects at most 10 sequences outside the USA from the
background_dataandreference_datainputs.As with the
usa_contextabove, this rule prioritizes sequences for the global context that are genetically similar to sequences in thecustom_sample.
Visualize the results
Run this command to start the Auspice server, providing auspice/ as the directory containing output dataset files:
nextstrain view auspice/
Navigate to http://127.0.0.1:4000/ncov/idaho. The resulting dataset should show the Idaho sequences against a backdrop of historical sequences: